Volume 4, Issue 16
June 26, 2014
Lessons from my day job
One of the benefits of my day job as a media researcher is that I gain valuable insight into what sorts of things I should create in the future to carry the messages of the Institute to as many people as are ready for it. My day job also enables me to do my ultimate passion work, which is to improve human effectiveness and thus happiness and/or fulfillment for the greatest number of people. The following post illustrates the synergy between my day job and my ultimate passion work.
The year: 1997. My company Next Century Media is working with John Hendrick’s innovative Discovery network and John Malone’s dominant cable operator TCI, installing addressable optimizer Opti*Mark into the National Digital Tech Center (NDTC) in Denver, for inclusion in the uplinking of dozens of TV networks to cable systems. This will make all the cable commercials potentially addressable to the set-top box (STB), will measure the STB, and offer program recommendations to subscribers on command.
The reasoning behind the program recommender is both to increase natural delight and also to give subscribers a cogent reason to feel better about their behaviors being tracked, albeit anonymously.
A technology favored at that time for recommendation engines — and still used today — is the collaborative filtering technique (CFT). It’s not the Netflix method of slicing down programs/movies into 78,000 tiny sliver genres, like Humphrey Bogart WWII movies of the 40s, and then counting the incidence of these subgenre choices within each subscriber’s individual record to make recommendations of other properties in the subgenre cluster that have not been watched yet through Netflix. CFT is the familiar “people who have bought this book also bought this other book”. NCM did not want to use CFT although it was ready to go off the shelf and cheap, not to mention accepted.
NCM wanted a method that would yield insight about people’s preferences, not just the facts of their observed choices.
Also, CFT takes a while to build a database and cannot give recommendations for a new show until there is some history of who watched it and who didn’t. With the importance of new shows to TV ad planners and programmers there was no way to live with CFT’s delay. So NCM created a keyword-driven system (today like so many other things called Bayesian). We compiled 1500 or so different words that are used to describe TV programs, ads and movies — screen content. Some of this came from work I had done consulting for the launches of cable networks, some had been from movie work I did with studios, and some was the result of many researchers pooling their knowledge.
One day the late Gerry Despain, who led the dozen software developers working on this, came to me and said he wanted to drop over 1200 of the keywords. I was aghast because test viewers were thanking us more than 9 to 1 in favor of the recommendations the system was producing. He said, “You don’t understand. I just want to drop the ones that do not predict set-top box data.” I saw that he was right and approved the efficiency move.
Later it gradually dawned on me the utter enormity of what had just transpired. We had stumbled on 250-300 words that DO predict the choices people make as to what to watch and what not to watch. Nowadays, in finally having the time to continue that line of development, we are calling those golden terms DrivertagsTM (DtagsTM for short) because the modern screenworld name for such descriptors is “metatags” — and because these 250-300 metatags are the first we know of that actually do appear to describe inner motivational states that predict real world behavior. Specifically, what we choose to watch on screens.
This would be merely a very important discovery in one group of businesses in the private sector. However, if we zoom out, we see that today’s civilization on Earth is in the process of becoming totally dominated by screen content. This is the latest evolution of the information acceleration process we call Acceleritis™, which my theory attributes to the advent of written language.
The primary devices with screens on which there is content, used by most of us in civilization today, are the computer, TV set, tablet, and mobile phone. People with enough money (or enough credit) are making sure they have at least one of each. Monied households with large families are accumulating screens perhaps faster than anyone in the household can count or cares to. Moreover, by any researcher’s count, the average person now spends more than half their waking hours with eyes on these screens.
The Human Effectiveness Institute (THEI) will be working with ScreenSavants, the private sector startup licensing NCM’s IP in this area, to make applications of learning to our Mission of increasing human effectiveness. We’ll be studying how specific DTags identify viewers more prone to Observer state or Flow state. We’ll be networking with interested academics including people who are working in nearby inquiries such as explaining the attraction of viewers to specific characters, deriving psychological insight from natural language utterances, linking screen content to higher values, semantic mapping, and all forms of related psycholinguistics. One reason for doing this is simply to understand — pure science. The other is for practical application to the mission of THEI, improving human effectiveness. We’ll report our progress here.
For a first example, consider the following graph. What does it mean?
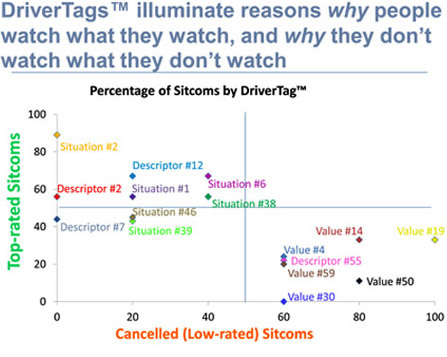
The easiest way to explain a graph is to explain what one datapoint means. In the upper left you’ll see “Situation #2”. That is a particular DTag — and 9 out of 10 top-rated situation comedies have that DTag. None of the cancelled sitcoms have that DTag. Now look at the lower left and you’ll see “Value #50” — 8 out of 10 cancelled sitcoms have that DTag, but only 1 of the top 10 rated sitcoms has it.
If I were investing $2.5 million per average new TV series pilot I would love to know which DTags are vital to success and which drive failure. That is the business reason for all this.
For psychology, given that the biggest use of time in our civilization is screen usage, discovering the motivators of this preponderant activity yields considerable new insight into what motivates people in our culture today. That’s the science reason for it.
The attachment of DTags to TV shows happened long before the analysis of ratings and cancellations. The same DTags that worked in 1997 are still working in 2014. On the inside we haven’t changed so much.
This is the kind of science I personally get to do that is part of my passion work. I’m a very lucky guy.
The gratitude attitude and admission that the Universe may indeed be sentient are the causes I attribute to such great luck. Hope you are very lucky too!
All my best,
Bill
Follow my regular blog contribution at Jack Myers Media Network: “In Terms of ROI.” It is in the free section of the website at Bill Harvey at MediaBizBloggers.com.
My new book, You Are The Universe: Imagine That is now available. Read an excerpt and watch my videos where I talk about the book.
